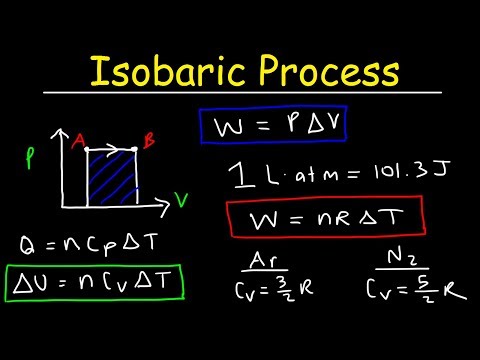
Where and have been used to denote the specific heats for one kmol of gas and is the universal gas constant.
Change in specific internal energy formula.
Internal energy formula concept of internal energy.
The change in the internal energy of a system is the sum of the heat transferred and the work done.
If a certain amount of heat is applied to gas the result is that the temperature of the gas may increase or else the volume of gas might increase.
Internal energy u the third component of our closed system energy equation is the change of internal energy resulting from the transfer of heat or work.
For a temperature change at constant volume dv 0 and by definition of heat capacity d q v c v dt.
The specific heat ratio or is a function of only and is greater than unity.
This is the change in internal energy.
31 the above equation then gives immediately 32 for the heat capacity at constant volume showing that the change in internal energy at constant volume is due entirely to the heat absorbed.
With the interactions of heat work and internal energy there are energy transfers and conversions every time a change is made upon a system.
Internal energy refers to all the energy within a given system including the kinetic energy of molecules and the energy stored in all of the chemical bonds between molecules.
Internal energy formula is the heat energy stocked in gas.
The heat flow is equal to the change in the internal energy of the system plus the pv work done.
An ideal gas with specific heats independent of temperature and is referred to as a perfect gas for example monatomic gases and diatomic gases at ordinary temperatures are considered perfect gases.
When the volume of a system is constant changes in its internal energy can be calculated by substituting the ideal gas law into the equation for δu.
Specific energy or massic energy is energy per unit mass it is also sometimes called gravimetric energy density or just energy density though energy density more precisely means energy per unit volume it is used to quantify for example stored heat and other thermodynamic properties of substances such as specific.
It keeps account of the gains and losses of energy of the system that are due to changes in its internal state.
The internal energy is measured as a difference from a.
Consider for example the following solved problem.
To understand the relationship between work and heat we need to understand the factor of linking factors.
In this manner doing some work externally or volume and temperature may both intensify but it will be made definite by the situations.
We cannot create nor destroy energy but we can convert or transfer it.
So if we add our heat and our work here we get that the overall change in internal energy for this process is negative 460 joules.
Energy density has tables of specific energies of devices and materials.