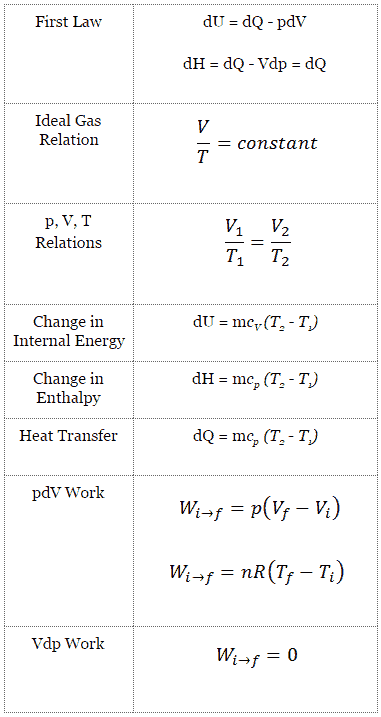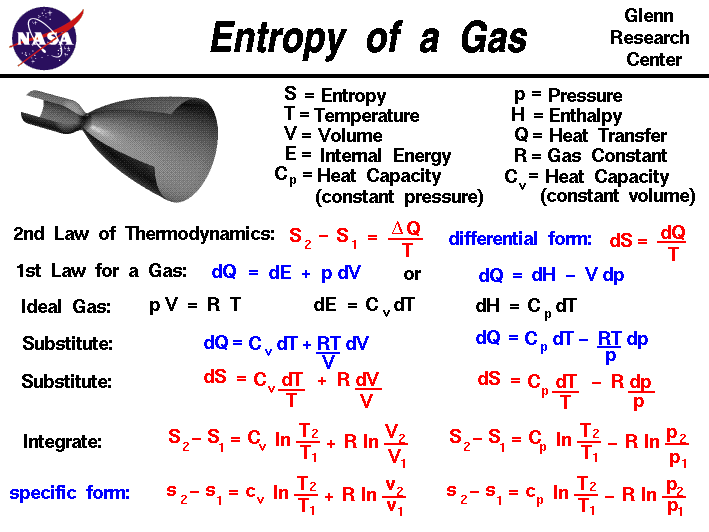The internal energy of a thermodynamic system is a measure of the energy within it excluding the kinetic energy of motion of the system as a whole and the potential energy of the system as a whole due to external force fields.
Change in internal energy formula constant pressure.
Specific heat is a property related to internal energy that is very important in thermodynamics.
The change in the internal energy of a system is the sum of the heat transferred and the work done.
Specific heat at constant volume and constant pressure.
It is usually formulated by stating that the change in the internal energy of a closed system is equal to the amount of heat supplied to the system minus the amount of work done by the system on its surroundings.
The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy u for a system is equal to the heat added to the system q minus the work done by the system w or in symbols.
The heat given off or absorbed when a reaction is run at constant volume is equal to the change in the internal energy of the system.
This article uses the physics sign convention for work where positive work is work done by the system.
The internal energy is measured as a difference from a.
P is gas pressure v is volume is the number of moles r is the universal gas constant 8 3144 j ok mole and t is the absolute temperature.
If you are working with an ideal gas mixture for which the internal energy of the reactants and products is not a function of pressure the change in internal energy in going from reactants to products at constant temperature and volume is the same as the change in internal energy in going from reactants to products at constant temperature and pressure.
The first law of thermodynamics the conservation of energy may be written in differential form as.
Where the subscripts v and p denote the variables held fixed.
When the volume of a system is constant changes in its internal energy can be calculated by substituting the ideal gas law into the equation for δu.
The heat transferred to the system does work but also changes the internal energy of the system.
The heat flow is equal to the change in the internal energy of the system plus the pv work done.
U q w u q w.
It keeps account of the gains and losses of energy of the system that are due to changes in its internal state.
The first law of thermodynamics is a version of the law of conservation of energy specialized for thermodynamic systems.
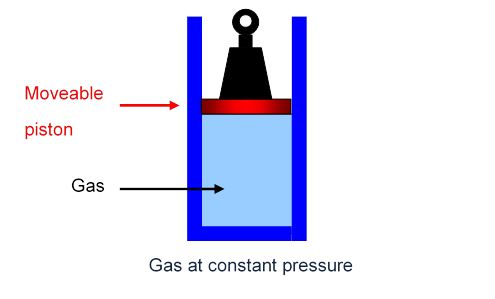
An isobaric process is a thermodynamic process in which the pressure stays constant.